Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Colors of Nature
Cross-polarized microscopy image of multilayered film consisting of alternate layers of an anti-cancer drug ellipticine and an edible polysaccharide polymer, pullulan. The nanothin film, produced by successive shearing of the drug and polymer solutions on silicon, embraces a magnificent morphology with needles and spherulites, that evokes colorful elements of nature unique to spectator’s imagination.
Department of Chemistry
Nanoprism Mosaic
A false colored SEM image of gold nanoprisms. The 2D gold nanostructures were synthesized using iodide as the capping agent which allows the final nanoparticles to be only a few nm thick and hundreds of nm in size. Excess gold precursor results in nanoprisms of different sizes.
Departments of Chemistry and Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
A Pop Art Perspective on Silicon Solar Microcells
Taken on an optical microscope, this image of a silicon solar microcell array was edited in ImageJ. Given the varying oxide thicknesses, the silicon dioxide layers are vibrantly colored when viewed under the microscope, and this image attempts to abstractly re-create that which is lost upon rendering into a black-and-white snapshot.
Department of Chemistry
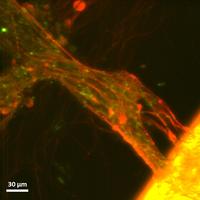
Solar Flare
Confocal fluorescence micrograph of primary dorsal root ganglion cells cultured on a 3D hydrogel scaffold. The neurons (red) and supporting glia (green) form complex tissue constructs that latch on to the edge of the highly fluorescent scaffold, resembling the release of plasma from the solar corona during a solar flare.
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Supramolecular Fibers
AFM image of self-assembled supramolecular fibers consisting of pi-conjugated oligopeptide. Upon fast evaporation of polar solvent, synthetic pi-conjugated oligopeptides spontaneously self-assembled into supramolecular fibers due to directional hydrogen bonding and pi-pi stacking interactions.