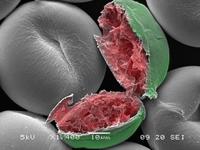
An SEM of gold nanoparticles (seen around the outside of the image) on an aluminum filter. The distortion in the center of the image is a reflection of the pole piece inside the SEM.
An illustration of the various interaction sites targeted by Nuclear Receptor Alternative-Site Modulators (NRAMs) mapped onto a mixed modal rendering of a PPAR/RXR heterodimer bound to DNA. The individual sites are expanded to show detail and include (clockwise, from top right) the binding function-3 interaction site, coactivator binding groove, DNA-binding zinc-finger motifs, and the DNA response-element. Each site represents an alternative strategy to targeting the ligand binding pocket (top left) in modulating nuclear receptor function.
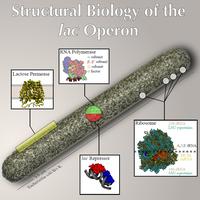
Structures of the molecules in the E. coli lac operon. RNA polymerase and the lac repressor compete for the lac promoter site on the DNA. After RNAP binds it produces lac transcripts, which are then translated by the ribosome. Lactose permease inserts into the membrane and imports lactose for food.
The diffusion of nano-particles couples to the long-ranged fluctuations of phospholipid tubes to which the particles attaches or couples to the collective breathing modes of actin networks in which the particles are entrapped.